Heart
The heart is a pump. The heart is a muscular organ about the size of a fist, located in the middle of the chest and tilted slightly to the left. The heart is divided into two parts, right and left.
This division of the heart prevents oxygen-rich blood from mixing with oxygen-poor blood. The deoxygenated blood returns to the heart after being circulated throughout the body.
The right side of the heart includes the right atrium and right ventricle, which collect blood and pump it into the pulmonary arteries to the lungs. The lungs update the blood with fresh oxygen. The lungs also excrete carbon dioxide as a waste product.
The oxygen-rich blood then enters the left side of the heart, which includes the left atrium and left ventricle. The left side of the heart pumps blood into the aorta to supply tissues throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients.
The heart muscle is supplied with blood by vessels called the coronary arteries. The blood supply to the heart and the activity of the heart muscle are somewhat like a supply and demand situation; the more active the heart is (for example, during intense physical activity or anxiety and stress), the more blood it needs. The coronary arteries must be able to supply this increased demand, or the heart muscle cells will run into trouble.
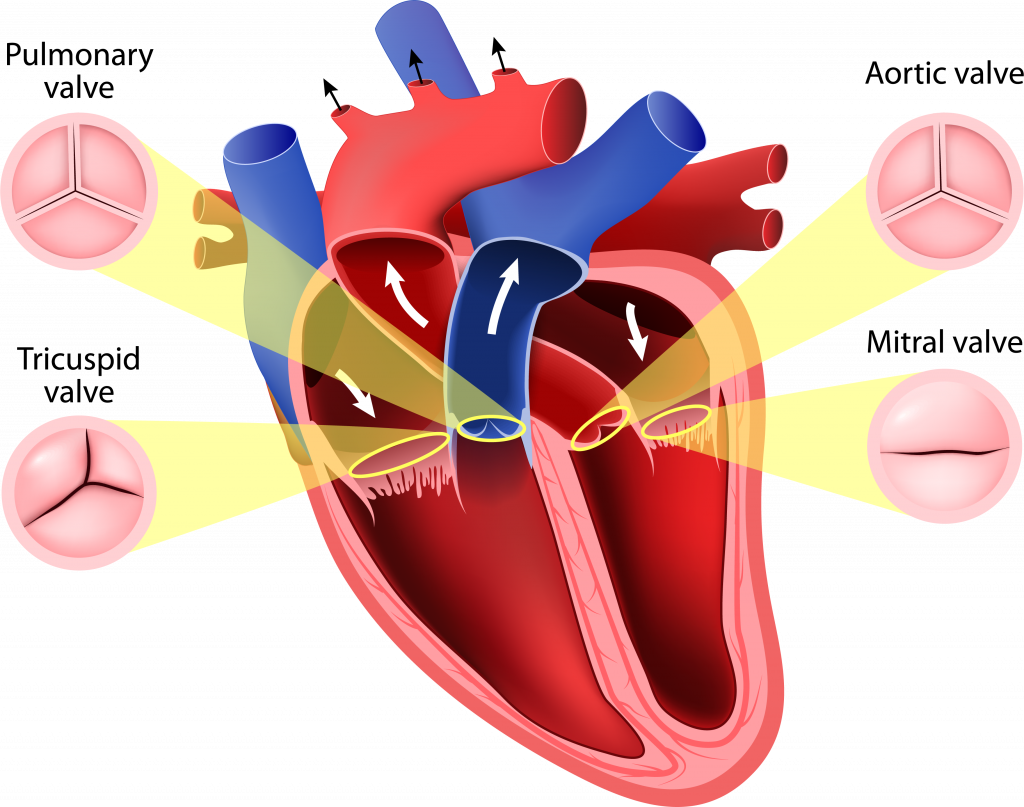
Heart valves
The four valves in the heart keep blood moving in the right direction by opening in one direction, even when needed.
In order to work properly, the valve must have the proper shape. This valve must be fully open and tightly closed so that no leakage occurs. The four valves are:
- Three naked
- mitral
- pulmonary
- Orty
Heart beats
The beating heart contracts and relaxes in a continuous cycle. During contraction (systole), the ventricles contract and send blood into the vessels to the lungs and body. During rest (diastole), the ventricles fill with blood flowing from the upper chambers of the heart (the left and right atria).
Electrical system
The heart’s nervous system keeps it beating and controls the constant exchange of oxygen-rich blood and oxygen-poor blood. This exchange keeps a person alive.
High-intensity electrical impulses start in the right atrium and reach the ventricles through special pathways to send the pulsating message to the heart.The heart’s conduction system causes the heart to beat in a normal, coordinated rhythm, keeping blood circulating.


Types of heart disease
Heart disease is a general term used for a wide range of heart conditions that can affect the heart muscle, valves, vessels, etc. The heart is basically a powerful, tireless pump. Some important heart diseases are:
1. Heart valve disease
2. Heart infections
3. Heart failure
4. Atherosclerosis
5. Irregular heartbeat
Reasons for creation Cardiovascular diseases
heart valve disease
There are many factors that cause heart valve disease. A person may be born with a valve disease or the heart valves may be damaged by conditions such as:
- rheumatic fever
- Infectious conditions (infective endocarditis)
- connective tissue disorders

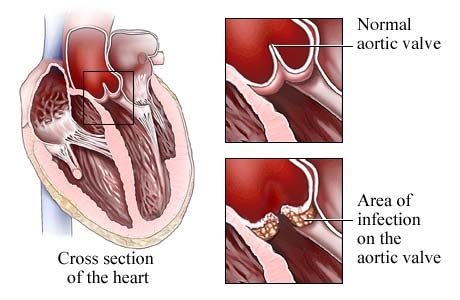
heart infection
Heart infections such as endocarditis occur when an irritant such as bacteria, viruses or chemicals infects the heart muscle. The most common causes of heart infections include:
- bacteria
- Viruses
- Parasites
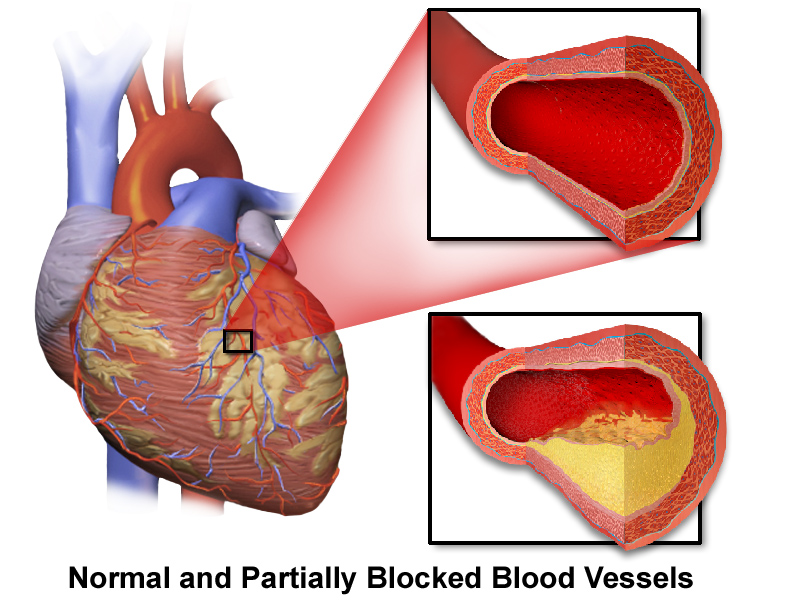
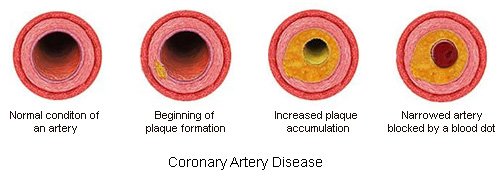
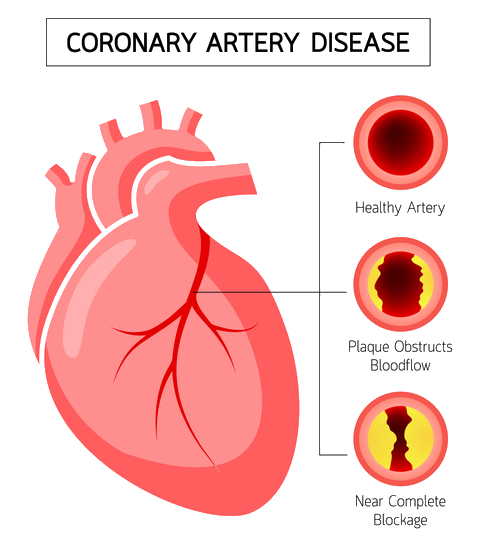
Atherosclerosis
The causes of heart disease vary depending on the type of disease. Cardiovascular disease can refer to different problems of the heart and blood vessels. This term often means damage to the heart and blood vessels. arteriosclerosisHe is.
This disease is the accumulation of fatty plaques in a person’s arteries. Plaque buildup causes the walls of the arteries to thicken and harden, which can block the flow of blood to the body’s tissues and organs through the arteries.
Atherosclerosis and the appearance of clots in the coronary arteries lead to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle cells. As a result of the lack of oxygen and nutrients and the accumulation of waste products in the heart muscle, pain known as “heart pain” or “angina” occurs. If the coronary artery is completely blocked (due to severe narrowing or a blood clot), the heart cells in the area of that artery will die, which is called a “heart attack”. Sometimes sudden death occurs as a result of severe and widespread malfunction of the heart muscle.
Atherosclerosis is also the most common cause of cardiovascular disease. This disease can be caused by correctable problems such as unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, being overweight and smoking.

Irregular heartbeat
Common causes of abnormal heartbeats (arrhythmias) or conditions that can lead to an irregular heartbeat include:
- Congenital heart defects that a person is born with.
- Coronary heart disease
- high blood pressure
- Diabetes
- smoking
- Excessive alcohol or caffeine intake
- drug
- Stress
- Some over-the-counter medications, prescription medications, nutritional supplements, and herbal remedies
- heart valve disease
A healthy person with a normal, healthy heart is less likely to develop a fatal arrhythmia without an external trigger (such as electrical shock or illicit drug use).
This is a first-degree arrhythmia: because a healthy person’s heart does not have any of the abnormalities (such as an area of scar tissue or scarring) that cause an irregular heartbeat.
However, in a diseased or deformed heart, the heart’s electrical impulses may not start well or spread throughout the heart, increasing the likelihood of an irregular heartbeat..
Complications of different types of heart disease
Complications of heart disease include:
heart failure
It is one of the most common complications of heart disease. Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. Heart failure can be the result of different types of heart disease including heart defects, cardiovascular disease, heart valve disease, heart infections or cardiomyopathy.
heart attack
If a blood clot blocks the flow of blood vessels that feed the heart, this condition causes a heart attack and loss or damage to part of the heart muscle. Atherosclerosis can cause a heart attack.
stroke
Risk factors that lead to cardiovascular disease can also lead to stroke. An ischemic stroke occurs when the arteries leading to the brain are narrowed or blocked, resulting in too little blood reaching the brain. A stroke is a medical emergency. In this condition, brain tissue begins to die within minutes after a stroke.
Aneurysm
It is a serious complication that can occur anywhere in the body. An aneurysm is a bulge in the wall of an artery. If an aneurysm ruptures, a person may experience life-threatening internal bleeding.
peripheral artery disease
Hardening of the arteries can also lead to peripheral artery disease. When a person has peripheral artery disease, their extremities (usually the legs) don’t receive enough blood flow. This condition causes symptoms, most notably leg pain when walking (claudication).
Sudden cardiac arrest
Stroke Sudden cardiac arrest is a sudden and unexpected loss of heart function, breathing, and consciousness, often caused by an irregular heartbeat. Sudden cardiac arrest is an emergency and if not treated promptly can be fatal, leading to sudden cardiac death.




Risk factors
Risk factors for heart disease include:
- Age
Aging increases the risk of damage and narrowing of the arteries and weakness and stiffness of the heart muscle.
- Gender
Men are generally at higher risk of heart disease. However, women’s risk increases after menopause.
- Family history
A family history of heart disease increases the risk of developing coronary artery disease, especially if a parent had it at a young age (before age 55 for male family members such as fathers and brothers and before age 65 for female family members such as mothers and sisters).
- smoking
Nicotine causes blood vessels to constrict, and carbon monoxide can damage the inner lining of the blood vessels, making them more susceptible to hardening of the arteries. Smokers are more likely to have heart attacks than nonsmokers.
- Certain chemotherapy and radiation therapy drugs for cancer treatment
Certain chemotherapy and radiation therapy drugs can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Poor diet
A diet rich in fat, salt, sugar, and cholesterol can contribute to heart disease.
- High blood pressure
Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to thickening and hardening of the arteries and narrowing of the vessels through which blood flows.
- High blood cholesterol levels
High blood cholesterol levels can increase the risk of plaque formation and atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes
Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease. Both conditions share common risk factors, such as being overweight and having high blood pressure.
- Overweight
Being overweight usually exacerbates other risk factors.
- Physical inactivity
Lack of exercise is also linked to many types of heart disease, as well as several of their risk factors.
- Stress
Unresolved stress can damage arteries and exacerbate other risk factors for heart disease.
- Poor hygiene
Sitting on your hands regularly and not engaging in other habits that can prevent bacterial or viral infections can put a person at risk for heart infections, especially if the person already has underlying heart disease. Poor dental health can also be linked to heart disease.
Different signs and symptoms of heart disease
1. 1. Xanthomas
بقع دهنيةSmall fatty spots on the eyelids, buttocks, elbows or knees, called xanthomas, are harmless in themselves; however, such fatty masses indicate the presence of too much cholesterol, so much that the vessels cannot hold it and, in order to maintain their balance, transfer it under the skin. Therefore, the vessels themselves need urgent help.
They are more likely to already have atherosclerosis, which can lead to bigger heart problems.
2. Yawning during sports activities
When the body sweats, it cools itself by evaporating moisture from the skin surface. However, our body also has other ways to cool itself, such as yawning, which helps to saturate the body with oxygen and reduce the temperature in the head. If the body’s natural mechanisms of thermoregulation cannot cope, we also yawn during exercise. The reasons for the disruption of thermoregulation can be diverse, and one of them is heart disease.
3. Bad breath
Gingivitis, or periodontal disease, can lead to bad breath and even tooth loss, but that’s not the only unfortunate consequence of gingivitis. New studies show that there is a link between gum disease and heart disease. The fact is that bacteria in inflamed gums can enter the cardiovascular system and cause inflammation there. The risk of heart disease is 20% higher in patients with periodontitis.
4. Blue and bruised lips
Even a healthy person’s lips can turn blue, for example, if the weather is very cold or they are at a high altitude. Physiologically, this is due to a decrease in blood circulation and a temporary lack of oxygen. If the lips turn blue for no apparent reason, then there is a problem with the blood flow in the body. Be sure to see a cardiologist to have your heart and blood vessels checked.
5. Change the shape of nails
If your nails start to thicken and become round, be sure to pay close attention to them. These changes indicate problems with your blood vessels. Most likely, your fingertips are not getting enough blood supply. In this situation, the nail cells strengthen their growth plates, trying to solve this problem.
Common Symptoms of Heart Disease That Doctors Recommend
severe stomach upset
Research has shown that some women experience indigestion problems a few days before having a heart attack, and they did not know that there was a link between digestive problems and heart attacks, so they did not seek solutions and treatment.
Confusion and boredom
Feeling confused, disoriented, or dull can be a sign of a blockage or heart valve problems, especially if accompanied by a feeling of fluttering (rapid heartbeat).
short breath
If even mild activity causes you to lose your breath, you should know that this is a serious problem, and you should compare your ability and activity today with what it was a year or two ago as a sign of the beginning of an important event. On the other hand, breathing problems that come to you even while lying down are serious and will be a problem in the future, and of course it can be a sign of heart valve problems, so be sure to consult a doctor.
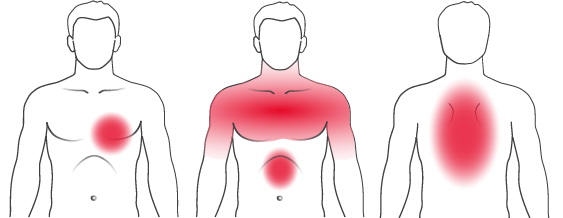
Chest pain
Perhaps the most common symptom of heart disease is severe pressure in the chest, like the feeling of a heavy object on the chest. This pain sometimes spreads to the shoulders, arms, neck and jaw. Chest pain after or during daily activity or stress can be a sign of problems with blood circulation.
flu-like conditions
Feeling nauseous or tired, getting colds, and sweating can be signs of inadequate blood flow and early signs of heart disease.
fatigue or insomnia
One of the things that people with heart problems raise after diagnosis is the problem of insomnia.And fatigue.





Living with heart disease
Most types of heart disease are chronic and develop slowly. These heart diseases start with minor symptoms and then gradually become severe. In most people, when heart disease begins, the person feels symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, ankle swelling, fluid retention, and other symptoms. Lifestyle changes (for example, having an oxygen capsule at home or reducing activity), surgery, or even a heart transplant may be necessary for the patient.
Drug therapy for heart disease
This treatment includes the use of medications that help reduce the severity and damage of the disease. These medications include:
- Antihypertensive drugs
- Medicines that reduce heart palpitations
- Cholesterol lowering medications
- Medications to stabilize heart rate
- Drugs to prevent blood clots in the coronary arteries
- Medications to improve blood flow in a person with heart disease
Other ways to treat heart disease include angioplasty, bypass surgery, or other surgeries.
 فارسی
فارسی العربية
العربية